deepredeff - from ‘deep learning prediction of
effectors’ is a package that contains trained deep learning models for
predicting effector proteins. deepredeff has been trained
to identify effector proteins using a set of known experimentally
validated effectors from either bacteria, fungi or oomycetes.
deepredeff has the following key features:
Highly accurate and general predictions.
Works on bacteria, fungi, oomycete sequences.
Supports different input formats - FASTA, data frame, AAString, AAStringset, and character string format.
Allows user to get quick summaries and plots of the prediction results they have.
Installation
First, we need to install the package itself by following the step below.
Install deepredeff
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("ruthkr/deepredeff")The deepredeff package uses TensorFlow which is
distributed as a Python package and so needs to be installed within a
Python environment on your system. Therefore, you need to have Python on
your system and the TensorFlow backend. If you already have TensorFlow
2.0.0 or later installed in your system, then you can specify the
environment where your TensorFlow is installed using
reticulate::use_condaenv().
If you do not have TensorFlow, then you can install it by simply following the step below.
Install TensorFlow
To install TensorFlow on your system, you need to run the following
commands. Note that this only needs to be run once, the
first time you use deepredeff.
This will provide you with an installation of Python and TensorFlow
suitable for use with the deepredeff R package. In
particular, this command will download and install Miniconda, and create
the r-reticulate environment in the following
locations:
GNU/Linux:
/home/<user>/.local/share/r-miniconda/envs/r-reticulatemacOS:
/Users/<user>/Library/r-miniconda/envs/r-reticulateWindows:
C:/Users/<user>/AppData/Local/r-miniconda/envs/r-reticulate
Sample data
Sample data that will be used here is a set of acterial proteins provided within this package. These sample data contain ten different protein sequences in FASTA format. These data can be loaded as follows:
library(deepredeff)
# Define the fasta path from the sample data
bacteria_fasta_path <- system.file(
"extdata/example", "bacteria_sample.fasta",
package = "deepredeff"
)
bacteria_fasta_path
#> [1] "/usr/local/Cellar/r/4.0.0/lib/R/library/deepredeff/extdata/example/bacteria_sample.fasta"Effector prediction
Once the data are loaded, you can predict them using the main
function predict_effector(). Since it is known that the
sample data are bacterial protein, then we can use the model trained on
bacterial effectors by choosing taxon = "bacteria".
Effector prediction with the sequences can be done as follows:
# Predict the effector candidate using bacteria model
pred_result <- predict_effector(
input = bacteria_fasta_path,
taxon = "bacteria"
)
#> Loaded models successfully!
#> Model used for taxon bacteria: ensemble_weighted.
# View prediction results
pred_result %>%
dplyr::mutate(name = substr(name, 1, 25),
sequence = substr(sequence, 1, 25))
#> name sequence s_score prediction
#> 1 tr|A0A0N8SZV2|A0A0N8SZV2_ MPINRPAFNLKLNTAIAQPTLKKDA 0.94834236 effector
#> 2 tr|A5CLR7|A5CLR7_CLAM3 Pa MQFMSRINRILFVAVVSLLSVLGCC 0.07981774 non-effector
#> 3 sp|B2SU53|PTHX1_XANOP TAL MDPIRSRTPSPARELLPGPQPDRVQ 0.99433611 effector
#> 4 tr|C0SPN9|C0SPN9_RALSL Un MSIGRSKSVAGASASHALASGENGS 0.84184432 effector
#> 5 tr|D2Z000|D2Z000_RALSL Ty MPPPIRNARTTPPSFDPSAAGDDLR 0.99537852 effector
#> 6 tr|Q8XX20|Q8XX20_RALSO Pu MSHMTFNTWKAGLWRLAAAAVLSLL 0.06455158 non-effector
#> 7 tr|Q87UH8|Q87UH8_PSESM Ta MKLHFSLRLLTALSLTGATFLAQAA 0.04928582 non-effector
#> 8 tr|Q4ZTI0|Q4ZTI0_PSEU2 Am MHRGPSFVKACAFVLSASFMLANTV 0.30616181 non-effector
#> 9 tr|Q4ZR15|Q4ZR15_PSEU2 Se MRRQPSLTLRSTLAFALVAMLTVSG 0.07221440 non-effector
#> 10 tr|D4I1R4|D4I1R4_ERWAC Ou MLSSNRRLLRLLPLASLLLTACGLH 0.04899144 non-effectordeepredeff will give you a dataframe object contains
four different columns:
-
name: the sequence identifiers. -
sequence: the input sequences. -
s_score: The prediction scores. A value between 0 and 1 that indicates the models level of belief that this sequence is an effector. -
prediction: class predictions obtained froms_scoreusing the standard 0.5 threshold, ifs_score >= 0.5prediction iseffector, else prediction isnon-effector
Summary and plot
After getting the prediction results, you can see information on all
the prediction results as a whole by running summary():
summary(pred_result)
#> Total sequences in input data: 10
#> ---
#> Taxon chosen: bacteria
#> Model type used: ensemble_weighted
#>
#> Total sequences predicted as effector: 4
#> Total sequences predicted as non-effector: 6We can see information on the number of sequences predicted as effectors and non-effectors and the model parameters used.
You can also plot the density distribution of the
s_scores results by running plot():
plot(pred_result)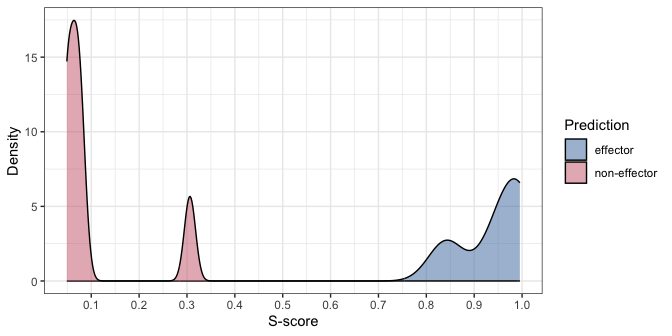
Here we can see that there is a good separation between the scores of predicted effectors and non-effectors.